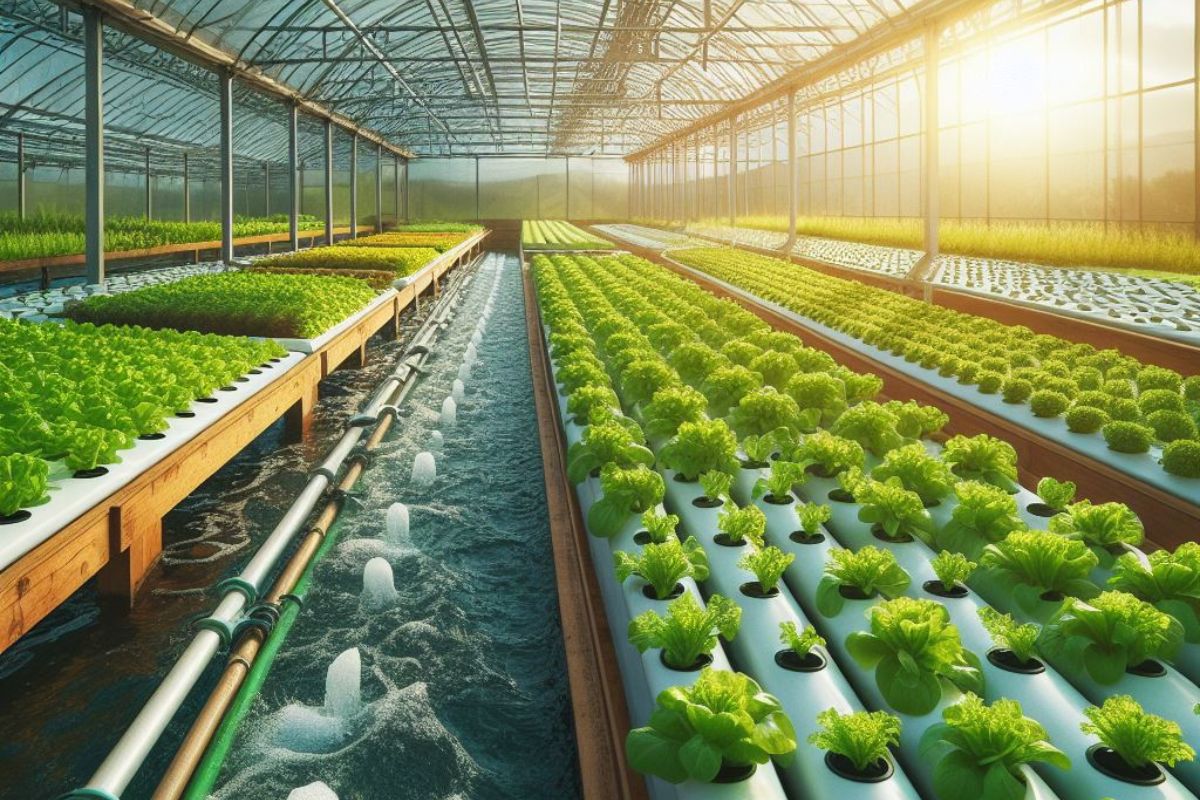
Aquaponics is a sustainable farming method that combines aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil) in a symbiotic environment. In this setup, fish waste serves as nourishment for plants, while the plants reciprocate by cleansing the water for the fish, establishing a self-sustaining ecosystem.
Brief Overview of Aquaponics Farming
Aquaponics farming involves the cultivation of aquatic organisms, typically fish, and various types of plants in a controlled environment. The process begins with fish, such as tilapia or trout, which are raised in tanks. As the fish produce waste, primarily ammonia, it accumulates in the water. This nutrient-rich water is then pumped into beds or channels where plants are grown hydroponically. The plants absorb the nutrients, effectively filtering the water, which is then recirculated back to the fish tanks, completing the cycle.
This integrated system offers several advantages over traditional farming methods, including efficient resource utilization, higher crop yields, and minimal environmental impact. Additionally, aquaponics requires less water compared to conventional agriculture, making it particularly suitable for regions facing water scarcity.
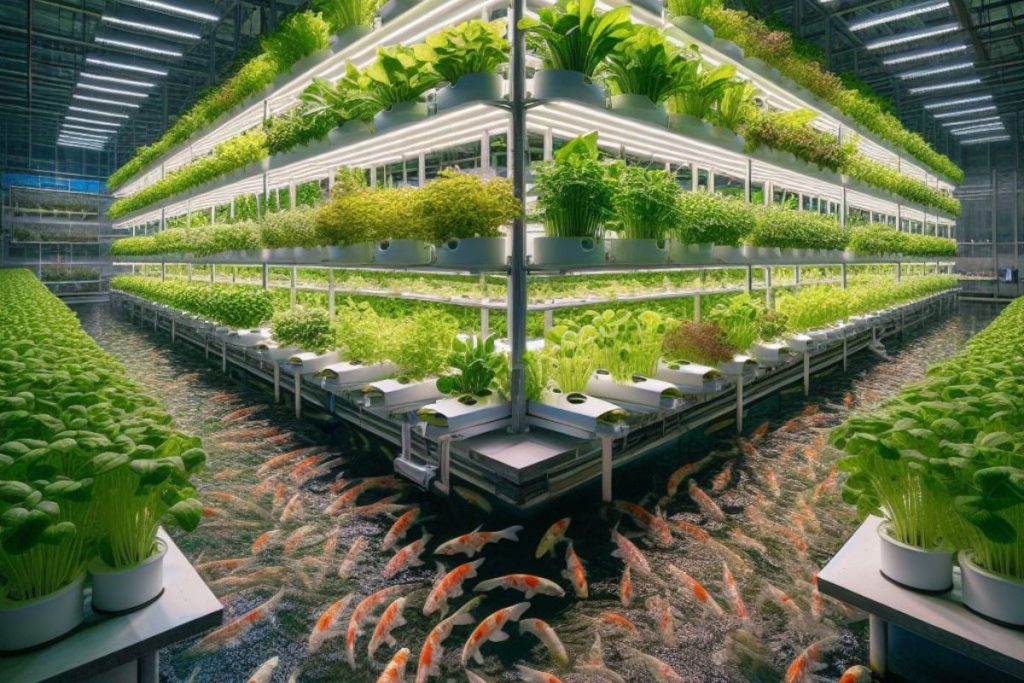

Importance of Starting Small for Beginners
For beginners, starting small in aquaponics is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows newcomers to gain hands-on experience and learn the intricacies of managing an aquaponics system without overwhelming themselves with a large-scale operation. Starting small enables beginners to understand the nuances of maintaining water quality, managing fish health, and optimizing plant growth.
Moreover, beginning with a small-scale setup minimizes the initial investment required. Aquaponics systems can vary in complexity and cost, and starting on a smaller scale allows beginners to test the waters before committing significant resources. It also provides an opportunity to experiment with different fish and plant species to determine which combinations work best for their specific environment and goals.
Furthermore, starting small allows beginners to gradually scale up their operation as they become more confident and proficient in aquaponics farming practices. This incremental approach reduces the risk of costly mistakes and increases the likelihood of long-term success in sustainable food production.
Understanding Aquaponics
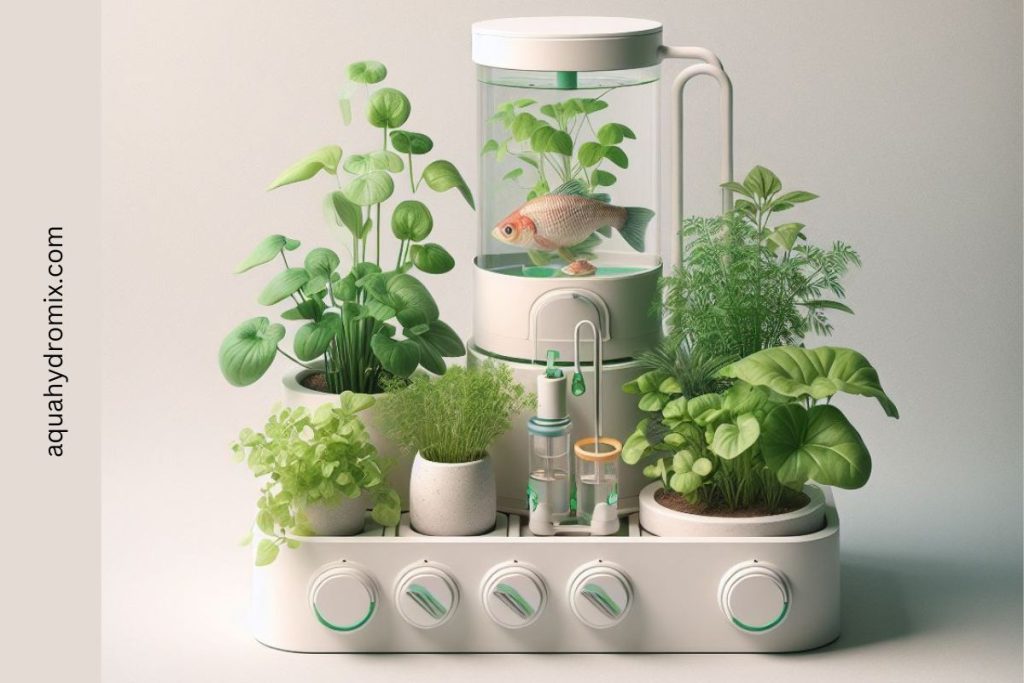

Explanation of the Aquaponics System:
Aquaponics is a closed-loop system that combines aquaculture and hydroponics in a symbiotic environment. In this system, fish are raised in tanks where they produce waste, primarily in the form of ammonia. This nutrient-rich water is then circulated to grow beds or channels where plants are cultivated hydroponically. The plants absorb the nutrients from the water, effectively filtering it and removing harmful substances. The purified water is then recirculated to the fish tanks, completing the cycle. This symbiotic relationship between fish and plants creates a sustainable ecosystem where both thrive and support each other’s growth.
Components of an Aquaponics System:
Fish Tank:
- The fish tank is the central component of the aquaponics system where aquatic organisms such as fish are raised.
- It should be large enough to accommodate the desired quantity and species of fish, with adequate filtration and aeration systems to maintain water quality.
- The fish tank serves as the source of nutrients for the plants in the system.
Grow Beds:
- Grow beds are containers filled with a growing medium (such as gravel, clay pellets, or rock wool) where plants are cultivated.
- The nutrient-rich water from the fish tank is pumped into the grow beds, providing essential nutrients for plant growth.
- The plants’ roots absorb the nutrients from the water, effectively filtering it before it is returned to the fish tank.
Water Pump:
- A water pump is used to circulate water between the fish tank and the grow beds.
- It ensures a constant flow of nutrient-rich water to the plants and maintains proper oxygenation levels for the fish.
Plumbing System:
- The plumbing system consists of pipes, valves, and fittings that connect the various components of the aquaponics system.
- It facilitates the movement of water between the fish tank, grow beds, and water pump, ensuring efficient water circulation and distribution.
Benefits of Aquaponics Farming:
Sustainable Agriculture:
- Aquaponics promotes sustainable agriculture by utilizing natural processes to maintain a balanced ecosystem.
- It minimizes the need for external inputs such as synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, reducing the environmental impact of food production.
Efficient Use of Resources:
- Aquaponics maximizes resource utilization by recycling water and nutrients within the system.
- It requires significantly less water compared to traditional farming methods and can be implemented in various environments, including urban areas with limited space.
Organic Produce:
- Since aquaponics relies on natural processes and avoids the use of chemical inputs, it produces organic, pesticide-free fruits, vegetables, and fish.
- This makes aquaponically grown produce appealing to health-conscious consumers and those seeking environmentally friendly food options.
Minimal Waste Production:
- Aquaponics generates minimal waste as the by-products from fish farming (waste and uneaten feed) are converted into nutrients for plant growth.
- It eliminates the need for waste disposal and reduces pollution, making it an environmentally sustainable farming practice.
Planning Your Aquaponics Farm
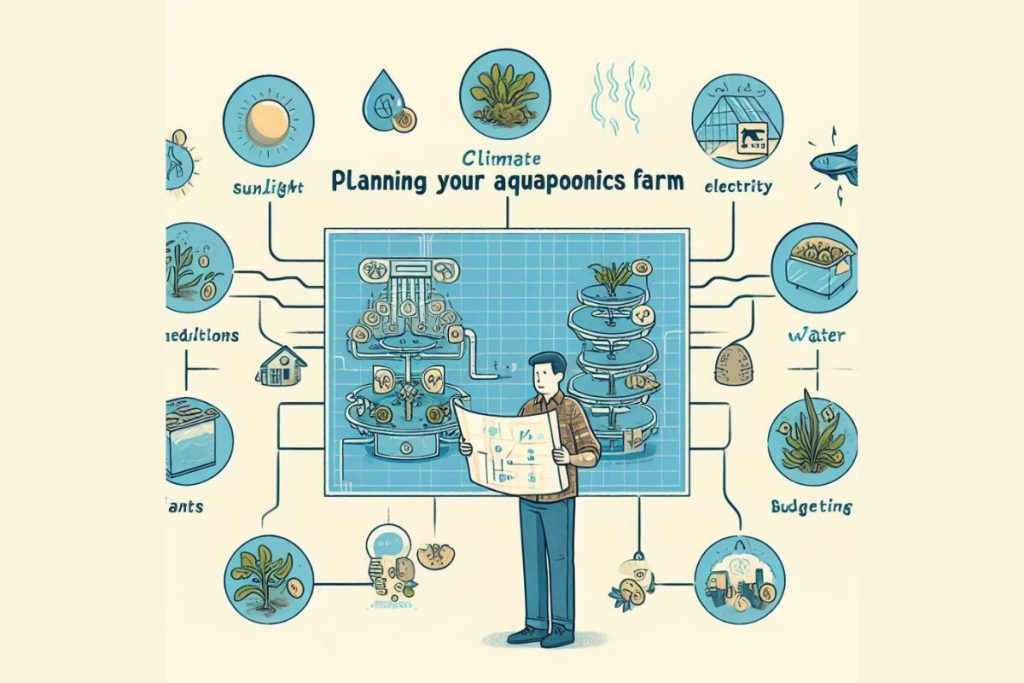
Location Considerations:
When planning your aquaponics farm, selecting the right location is crucial for the success of your operation. Considerations include access to sunlight, climate conditions, and available space. Ideally, choose a location with ample sunlight exposure for optimal plant growth. Additionally, ensure the area is sheltered from strong winds and extreme temperatures to maintain stable conditions for both fish and plants. Accessibility to water and electricity is also essential for the efficient operation and maintenance of your aquaponics system.
Designing Your Aquaponics Setup:
Determining System Size:
Before setting up your aquaponics system, determine the appropriate size based on your available space, resources, and production goals. Consider factors such as the number of fish and plants you intend to cultivate, as well as the desired output of your farm. Starting small and gradually expanding allows for easier management and experimentation, especially for beginners.
Choosing Appropriate Fish and Plants:
Selecting suitable fish and plants is crucial for a thriving aquaponics system. Consider factors such as temperature tolerance, nutrient requirements, and market demand when choosing fish species. Common choices include tilapia, trout, and catfish. Similarly, select plants that thrive in hydroponic conditions and complement the fish species chosen. Popular choices include leafy greens like lettuce, and herbs, and certain fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers.
Calculating Water and Nutrient Requirements:
Calculate the water and nutrient requirements of your aquaponics system to ensure optimal conditions for fish and plant growth. Factors to consider include the stocking density of fish, plant density, and nutrient cycling rates. Additionally, consider water loss due to evaporation and transpiration, and plan for replenishment accordingly. Monitoring and maintaining water quality parameters such as pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels are essential for the health of both fish and plants.
Setting a Budget:
Establishing a budget is essential to plan and manage expenses for your aquaponics farm. Consider costs associated with equipment, materials, fish, plants, utilities, and ongoing maintenance. Research and compare prices for components such as fish tanks, grow beds, water pumps, plumbing, and lighting systems. Factor in additional expenses for tools, testing kits, and potential unforeseen expenses. Setting a realistic budget helps prioritize spending and ensures the financial sustainability of your aquaponics venture.
By carefully considering location, designing your aquaponics setup, and setting a budget, you can effectively plan and establish a successful aquaponics farm tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Building Your Aquaponics System
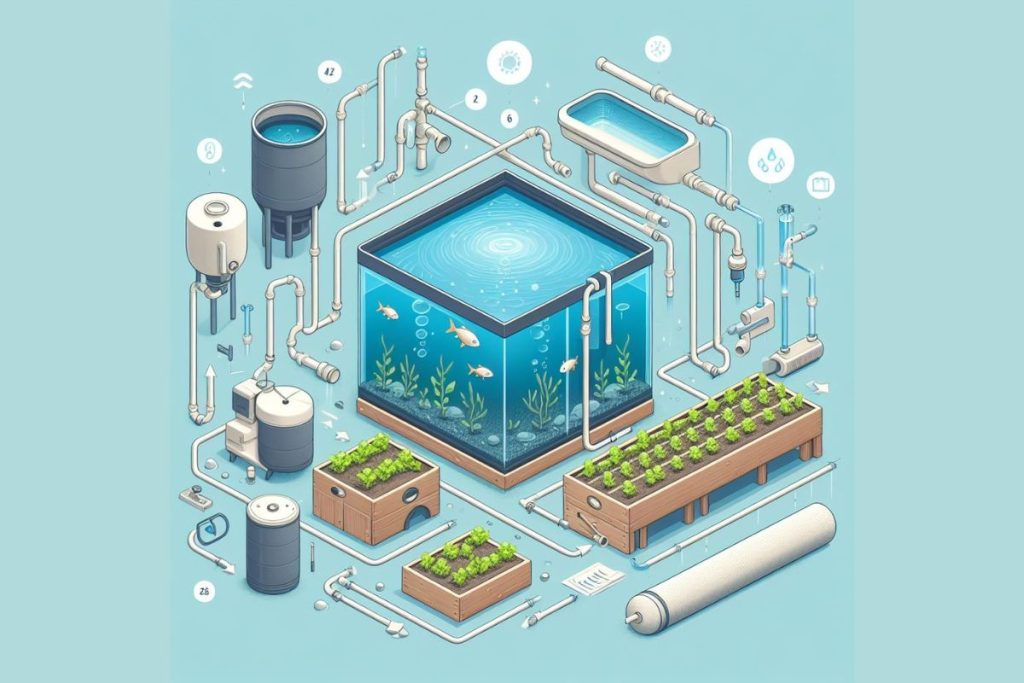
Step-by-Step Guide to Constructing Your System:
Building the Fish Tank:
- Choose a durable and waterproof container for your fish tank, such as a fiberglass or food-grade plastic tank.
- Ensure the tank is large enough to accommodate the desired number and species of fish, with adequate depth and surface area.
- Install a sturdy support base to bear the weight of the tank and water.
- Ensure all seams or joints are sealed tightly to avoid any leaks.
- Set up a reliable filtration system to maintain water quality and remove solid waste.
Assembling Grow Beds:
- Select grow beds made from non-toxic materials such as food-grade plastic or treated wood.
- Determine the size and number of grow beds based on available space and desired plant production.
- Fill grow beds with a suitable growing medium such as expanded clay pellets or gravel.
- Install a flood and drain irrigation system, allowing water to cycle through the grow beds and back into the fish tank.
- Consider incorporating bell siphons or other mechanisms to regulate water flow and prevent overflooding of the grow beds.
Installing Plumbing and Water Pump:
- Design a plumbing system to facilitate the circulation of water between the fish tank and grow beds.
- Install a water pump to move water from the fish tank to the grow beds, ensuring adequate nutrient distribution to the plants.
- Include valves and fittings to control water flow and adjust system pressure as needed.
- Test the plumbing connections for leaks and proper functionality before adding water to the system.
Adding Necessary Components (Aeration, Filtration, etc.):
- Integrate aeration systems such as air pumps and diffusers to oxygenate the water and promote fish health.
- Incorporate mechanical and biological filtration components to remove particulate matter and maintain water clarity.
- Consider adding supplementary heating or cooling systems to regulate water temperature within optimal ranges for both fish and plants.
- Install sensors and monitoring devices to track water parameters such as pH, ammonia levels, and temperature, enabling timely adjustments and intervention as needed.
Tips for Ensuring System Functionality and Efficiency:
Water Quality Management:
- Consistently check water quality parameters such as levels of ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and dissolved oxygen.
- Conduct routine water tests and adjustments to maintain optimal conditions for fish and plant growth.
- Implement water changes or partial system flushes as necessary to prevent nutrient buildup and maintain system balance.
Monitoring pH Levels:
- Monitor pH levels regularly using a reliable pH meter or test kit.
- Maintain pH within the appropriate range for both fish and plants, typically between 6.8 and 7.2.
- Adjust pH using safe buffers or additives as needed to prevent fluctuations and ensure stable conditions.
Temperature Control:
- Install temperature monitoring devices to track water temperature fluctuations.
- Maintain water temperature within the suitable range for fish species and plant growth, typically between 75°F to 85°F (24°C to 29°C).
- Utilize insulation, shading, or heating/cooling systems to regulate temperature and minimize fluctuations caused by external factors.
By following these steps and tips, you can effectively build and maintain a functional and efficient aquaponics system for sustainable fish and plant production. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and adjustments are key to ensuring the health and productivity of your aquaponics farm.
Stocking Your Aquaponics Farm

Choosing Fish Species for Your System:
- Research different fish species suitable for aquaponics systems, considering factors such as water temperature, pH tolerance, and growth rate.
- Common choices include tilapia, trout, catfish, and perch, but options vary depending on regional availability and climate conditions.
- Select fish species that complement your desired plant species and environmental conditions to ensure a balanced ecosystem.
Selecting Suitable Plants for Cultivation:
- Choose plants that thrive in hydroponic conditions and have compatible nutrient requirements with your chosen fish species.
- Popular options include leafy greens like lettuce, herbs such as basil and mint, and fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers.
- Consider factors such as growth rate, space requirements, and market demand when selecting plant varieties for cultivation.
Introducing Fish and Plants to the System:
- Acquire healthy fish and plants from reputable suppliers or local aquaculture and nursery sources.
- Gradually introduce fish to the system, allowing them time to acclimate to the water parameters and environment.
- Plant seedlings or young plants in grow beds, ensuring proper spacing and nutrient availability for optimal growth.
- Monitor fish behavior and plant health closely during the initial stocking period to identify any potential issues and make necessary adjustments.
Maintaining Your Aquaponics Farm

Daily Maintenance Tasks:
Feeding Fish:
- Provide fish with appropriate feed according to their nutritional requirements and feeding schedule.
- Monitor fish feeding behavior to ensure all fish are receiving adequate nutrition without overfeeding.
- Checking Water Levels and Quality:
- Monitor water levels in the fish tank and grow beds, topping up as needed to maintain proper circulation and hydration for plants.
- Test water quality parameters such as pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels daily to ensure optimal conditions for fish and plant health.
Inspecting Plants for Pests and Diseases:
- Regularly examine plants for indications of pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies.
- Take prompt action to address any issues through organic pest control methods, nutrient supplementation, or pruning affected plant parts.
Weekly and Monthly Maintenance Routines:
Cleaning Grow Beds and Filters:
- Regularly clean grow beds and filtration components to remove debris, excess organic matter, and biofilm buildup.
- Replace or clean filter media as needed to maintain efficient water filtration and nutrient cycling.
Pruning Plants:
- Prune plants regularly to remove dead or diseased foliage, promote healthy growth, and maintain optimal plant density.
- Harvest mature plants as needed to encourage continuous production and prevent overcrowding.
Monitoring System Performance:
- Conduct routine system checks to ensure all components are functioning properly and efficiently.
- Monitor water flow, pump operation, and aeration levels to optimize system performance and troubleshoot any potential issues.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing Water Quality Problems:
- Identify and rectify sources of water quality issues such as high ammonia or nitrite levels, pH fluctuations, or inadequate oxygenation.
- Conduct water tests regularly to diagnose problems and implement appropriate corrective measures, such as water changes, pH adjustments, or nutrient supplementation.
Dealing with Plant Deficiencies:
- Identify nutrient deficiencies in plants through visual symptoms such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth.
- Adjust nutrient levels in the system by supplementing with appropriate fertilizers or organic amendments to address specific deficiencies.
- Ensure proper nutrient balance and availability for plants by maintaining optimal water quality and nutrient cycling in the aquaponics system.
Managing Pest Infestations:
- Monitor plants for signs of pest infestations such as insect damage, leaf discoloration, or abnormal growth patterns.
- Implement integrated pest management strategies, including cultural, mechanical, and biological control methods, to mitigate pest populations effectively.
- Use organic pest control products or natural predators to manage pest infestations while minimizing harm to fish and beneficial organisms.
Handling Fish Health Issues:
- Monitor fish behavior and physical condition for signs of stress, illness, or injury.
- Address fish health issues promptly by adjusting water parameters, improving water quality, or administering appropriate treatments under the guidance of a qualified aquatic veterinarian.
- Quarantine sick or injured fish as necessary to prevent the spread of diseases and facilitate recovery in a controlled environment.
Harvesting and Enjoying Your Produce
Harvesting Fish and Vegetables:
- Harvest fish at the appropriate size and maturity for optimal taste and texture, following safe and humane harvesting practices.
- Harvest vegetables and herbs when they reach peak freshness and flavor, taking care to minimize damage to plants and preserve quality.
- Harvest regularly to encourage continuous plant growth and maintain a steady supply of fresh produce throughout the growing season.
Tips for Storing and Cooking Your Produce:
- Store harvested fish and vegetables properly to maintain freshness and quality, following recommended storage guidelines for each product.
- Experiment with different cooking methods and recipes to enjoy your aquaponics produce in delicious and nutritious meals.
- Share your harvest with family, friends, or local community members to spread the joy of homegrown aquaponics produce.
Celebrating Your Aquaponics Success:
- Reflect on the achievements and lessons learned throughout your aquaponics journey.
- Share your experiences and knowledge with others through community events, workshops, or online forums to inspire and educate fellow aquaponics enthusiasts.
- Celebrate the sustainable and rewarding nature of aquaponics farming, recognizing the positive impact of your efforts on the environment, health, and well-being of yourself and others.
In conclusion, aquaponics farming offers a promising solution to the pressing challenges of food production, environmental sustainability, and community resilience. Through our discussion, we’ve highlighted the key components of aquaponics, from system setup to harvesting techniques, underscoring the importance of sustainability, efficiency, and responsible stewardship for long-term success.
To those considering embarking on their aquaponics journey, I wholeheartedly encourage leaping. This endeavor not only provides accessible, scalable opportunities but also offers invaluable educational experiences. For beginners, there exists a wealth of resources, support networks, and encouragement to navigate challenges and achieve success.

